Wallpaper Patterns

Wallpaper Patterns
Begin learning about Wallpaper Patterns with the Wallpaper Exploration.
A wallpaper pattern is a plane figure which has more than one direction of translation symmetry. Most actual wallpaper fits the bill, because it must repeat left to right in order to hang in strips, and it must repeat vertically so that multiple strips can be cut from the same roll.
Having one line of translation symmetry forced frieze patterns to be infinitely long strips. For wallpaper patterns, the multiple translation directions force the pattern to cover the entire infinite plane. A finite portion of a wallpaper pattern is enough to establish the translation symmetry which is used to extend to the entire plane. Generally, when drawing wallpaper patterns, show enough of the pattern so that the translation symmetries are obvious. Practically, it takes at least 9 repetitions of the pattern (in a 3x3 array) to clearly display the translation symmetry.
In a wallpaper pattern, the lattice of translations is the collection of all translated images of a point. To mark the lattice of translations, choose a point in the figure and then mark all translations of that point. Be careful not to mark reflected or rotated versions of the point.
The lattice is so named because connecting nearby dots with edges results in a grid, or lattice, structure. These lattice lines depend on which dots one chooses to connect, so they are not usually shown.
The example below is adapted from a pre-Columbian Peruvian fabric pattern. In the left portion, the basic pattern is shown. The center portion has the lattice marked with red dots, and the right portion connects nearby lattice points with lines to show that points lie on a rectangular grid.
Explorations
Start exploring wallpaper patterns with some of these explorations:
Create your own wallpaper patterns with:
Related explorations for tessellations are available in the later sections:
The Seventeen Wallpaper Groups
As with frieze groups, the classification of wallpaper symmetry groups is done by a process of elimination. The first crucial step is known as the crystallographic restriction:
A rotation symmetry of a wallpaper pattern must be a rotation of order 2, 3, 4, or 6.
Because two reflection axes which meet at an angle produce a rotation symmetry whose angle is , the crystallographic restriction also puts a strong restriction on the possible reflection and glide reflection symmetries. For example, if a wallpaper pattern has rotations of order 2 but no higher order rotations, then it can have at most two sets of reflection axes, meeting at right angles.
A painstaking and lengthy argument eventually reduces the possibilities down to 17 wallpaper symmetry groups. This remarkable classification was first published by the Russian mathematician Fedorov in 1891, but not widely recognized. George Pólya's rediscovery of the 17 groups in 1924 [1] brought the subject into the mainstream, and Escher read Pólya's work with great interest, hand copying Pólya's seventeen diagrams into his own notes. The adventurous reader will find a rigorous treatment of the classification in the #Related Sites section of this page.
| Symmetry Group - IUC | Lattice | Rotation | Reflection |
|---|---|---|---|
| p1 | Parallelogram | none | none |
| p2 | Parallelogram | 2 | none |
| pm | Rectangle | none | parallel |
| pg | Rectangle | none | none |
| cm | Rhombus | none | parallel |
| pmm | Rectangle | 2 | 90 degrees |
| pmg | Rectangle | 2 | parallel |
| pgg | Rectangle | 2 | none |
| cmm | Rhombus | 2 | 90 degrees |
| p4 | Square | 4 | none |
| p4m | Square | 4 + | none |
| p4g | Square | 4 * | 45 degrees |
| p3 | Hexagon | 3 | none |
| p31m | Hexagon | 3 * | 60 degrees |
| p3m1 | Hexagon | 3 + | 30 degrees |
| p6 | Hexagon | 6 | none |
| p6m | Hexagon | 6 | 30 degrees |
+ = all rotation centers lie on reflextion axes
* = not all rotation centers lie on reflextion axes
The remainder of this section is a list of the 17 wallpaper symmetry groups, with their Crystallographic names, descriptions of their symmetries, and a sample of each.
Wallpaper Flow Chart
It can be quite difficult to find and mark all symmetries of a wallpaper pattern. However, it is possible to identify the symmetry group of a wallpaper pattern without finding all of its symmetries by focusing on the most important features. The idea of a flow chart for symmetry identification was introduced by Dorothy Washburn and Donald Crowe[2] as a tool for use in cultural anthropology. A version of their flow chart is recreated here.
To use the flow chart, begin with the rotation order question on the left, and follow arrows towards the right until the symmetry group is determined. Practice with the Wallpaper Symmetry Exploration.
Wallpaper Group Organization
Here is a way to organize the wallpaper symmetry groups that may provide another tool determining the symmetry group of a wallpaper pattern.
No rotations
- p1 No reflections and no glide-reflections.
- pg No reflections; with glide-reflections.
- pm With reflections; any glide-reflection axis is also a reflection axis.
- cm With reflections; some glide-reflection axis is not a reflection axis.
With 2-fold rotations but no 4-fold
- p2 No reflections and no glide-reflections.
- pgg No reflections; with glide-reflections.
- pmm With reflections; any glide-reflection axis is also a reflection axis.
- cmm With reflections; some glide-reflection axis is not a reflection axis but is parallel to a reflection axis.
- pmg With reflections; some glide-reflection axis is not a reflection axis and is not parallel to any reflection axis.
With 4-fold rotations
- p4 No reflections.
- p4m With reflections; 4-fold rotation centers lie on reflection axes.
- p4g With reflections; 4-fold rotation centers do not lie on reflection axes.
With 3-fold rotations but no 6-fold
- p3 No reflections.
- p3m1 With reflections; any rotation center lies on a reflection axis.
- p31m With reflections; some rotation center does not lie on any reflection axis.
With 6-fold rotations
- p6 No reflections.
- p6m With reflections.
Examples

This pattern is a common brick layout. What is its symmetry group?
Rows of bricks make horizontal strips that will remain horizontal after rotation, which means that the pattern has at most order 2 rotation. It does have order 2 rotation symmetry, for instance at the center of each brick. In the flow chart, starting at "Largest rotation order?", follow the arrow marked 2.
The pattern does have reflection symmetry, both horizontally and vertically, so in the flow chart the next two questions are answered yes.
The final question will determine if this pattern has symmetry pmm or cmm: Are all rotation centers on mirror lines?
This question may be hard to answer, because you need to find all the rotation centers. Looking at samples of pmm and cmm can help. In pmm, strips are aligned, while in cmm patterns, strips are staggered. That suggests that this brick layout has cmm symmetry group.
To confirm that the pattern has cmm symmetry, we need to find a rotation center not on a mirror line. There should be a piece of this pattern displaying C2 symmetry considered as a finite rosette, and we learned to recognize those by looking for details in the shape of the letters S or Z. Here, two bricks together make a sort of 'S':
The rotation center is marked, and is not on a mirror line.
This brick layout pattern has symmetry group cmm.
|
What is the symmetry group for Escher's Sketch #45 (Angels and devils)? The largest rotation order in this sketch is order 4, with centers at the point where the wings of four angels and four devils come together. Note that there are also rotation symmetries of order 2, but these are not relevant to the classification via the flowchart. There are reflections, both horizontally and vertically through the centers of the angels and devils, which by themselves have bilateral symmetry. On the flowchart, this leads to the question "Are there mirror lines intersecting at 45°?". Since the only reflection axes are horizontal and vertical, we answer 'no' and find that the symmetry group of this pattern is p4g. |
|
This example is from the 1856 catalog, The Grammar of Ornament (Egyptian No 7 (plate 10), image #20). The horizontal lines of white flowers and yellow waves prevent any rotation except for order 2, which this pattern does have. Notice that every yellow wave spirals clockwise towards its blue central dot, and there are no counterclockwise versions. This means that the pattern has neither reflection nor glide-reflection symmetry. It's symmetry group is p2. |
|
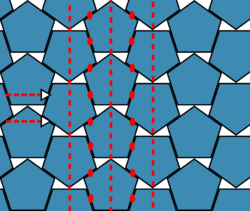
This pattern of pentagons has vertical mirror lines and order 2 rotations (marked in red in the picture). Since there are no other reflection lines, the flowchart determines this pattern to have symmetry group pmg. Symmetry group pmg should have glide reflections perpendicular to the mirror lines, and this pattern does, shown in the picture as the horizontal dashed arrows. Notice the glide reflections lie on the same lines as the rotation centers. Finally, it is important to note that there is no order 5 rotation in this pattern. Each pentagon alone would have D5 symmetry, but the order 5 rotation does not preserve the whole wallpaper pattern. With any rotation but 180°, the vertical stacks of pentagons would be tilted at a different angle. |
The Classification of Plane Symmetry Groups
All discrete symmetry groups of plane figures are completely classified.
Figures with no translation symmetry, the rosette patterns, have either cyclic or dihedral symmetry. There are infinitely many possibilities for the rosette groups because we can create a pattern for Cn and Dn respectively for any positive integer n.
Figures with one line of translation symmetry have one of the seven frieze groups for their symmetry. There are only limited possibilities for the types of symmetry that will leave a frieze pattern invariant.
Every figure with more than one line of translation symmetry falls into one of the 17 wallpaper symmetry groups. A rigorous proof is beyond the scope of this book, but the main outline of this argument is as follows:
- It is possible to create a pattern that will only allow translations. This would have a p1 symmetry group.
- Patterns that allow only rotations and translations have to be p2, p3, p4 or p6 groups.
- Patterns with glide reflections and translations only must be one of pg, pm or cm.
- Allowing both rotations and reflections or rotations and glide-reflections produces nine more groups: cmm, pmm, pmg, pgg, p4m, p4g, p3m1, p31m, and p6m.
George Baloglou has a detailed proof of the classification online.[3]
Escher's Use of Symmetry
In 1922 and again in 1936, Escher made visits to the Alhambra, a Moorish palace in Granada, Spain. The Islamic edict against images of the human form forced Moorish artists to develop a purely geometric style, so the Alhambra contains many examples of symmetric patterns. In fact, it is widely reported that the Alhambra contains examples of all 17 wallpaper groups[4] although a recent article by Grünbaum[5] calls this claim into question.
Upon his first visit, Escher wrote in his diary:
- The strange thing about this Moorish decoration is the total absence of any human or animal form –even, almost of any plant form. This is perhaps both a strength and a weakness at the same time[6].
One of Escher's breakthroughs as an artist was to create symmetric, plane-filling patterns out of recognizable figures, including human and animal forms. These patterns are laid out in his Regular Division of the Plane Drawings, which were sketched in notebooks and served as source material for his finished printed works.
The use of imagery from life led to restrictions on possible choices for symmetry for aesthetic reasons, restrictions which Escher gradually evolved over time. Examining the Regular Division of the Plane Drawings, one finds that the vast majority fall into one of seven symmetry groups: p1, p2, p3, p4, p6, pg, and pgg. These are exactly the symmetry groups which have no reflection symmetry - only translation, rotation, and glide reflection. If two creatures meet on a line of mirror symmetry, they must have a flat edge, and recognizable figures from life rarely have perfectly straight edges. Because of this, Escher mostly avoided mirror symmetry, although he did create a few drawings where bilateral symmetry of the motif leads to overall mirror symmetry of the pattern.
Some animal motifs, generally larger animals, are usually seen from the front or side, and so look silly when viewed upside down or at an angle. Escher's was careful, at least in his later work, to avoid symmetries containing rotation when working with such animals. On the other hand, Escher writes [7]:
- When a rotation does take place, then the only animal motifs which are logically acceptable are those which show their most characteristic image when seen from above.
For example, insects and lizards occur frequently in Escher's work when rotation symmetry is present.
Although Escher understood symmetry well and and knew of the mathematical classification of wallpaper symmetry groups from Polya's work, he was interested in creating new patterns rather than analyzing existing work. His technique, which will be explored in the next chapter, made little reference to symmetry groups.
Exercises
Relevant examples from Escher's work
- Escher's sketches of Polya's 17 wallpaper patterns. Visions of Symmetry, pg. 24-26.
- Escher's Regular Division of the Plane Drawings.
Related Sites
Theory
- Isometrica: A Geometrical Introduction to Planar Crystallographic Groups by George Baloglou.
- Proof of the 17 wallpaper group classification by George Baloglou.
- The Discontinuous Groups of Rotation and Translation in the Plane by Xah Lee.
Examples
- Wallpaper Groups pages on Pintrest, by Kjerste Christensen.
- Plane symmetry examples with symmetries marked, by Martin von Gagern.
- Tilings by Dror Bar-Natan.
- The 17 wallpaper groups (animated) by Hop.
- The 17 wallpaper groups shown with symmetries marked by Xah Lee.
- The 17 wallpaper groups by David Joyce.
Tools
- Java Kali applet by Mark Phillips.
- Morenaments applet and stand-alone software by Martin von Gagern.
- Escher Web Sketch applet from the Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne.
Notes
- ↑ Pólya,G. 1924. Über die Analogie der Kristallsymmetrie in der Ebene. Zeitschrift für Kristallographie 60, p278-282
- ↑ Washburn, D. and Crowe, D., Symmetries of Culture: Theory and Practice of Plane Pattern Analysis, University of Washington Press, 1988
- ↑ Baloglou G. 2002. A brief description and rigorous classification of the seventeen planar crystallographic groups. http://www.oswego.edu/~baloglou/103/seventeen.html
- ↑ Montesinos, Classical Tessellations and Three-Manifolds, 1987
- ↑ Grünbaum, What symmetry groups are present in the Alhambra?, Notices of the AMS 53(6), 2006
- ↑ Visions of Symmetry, pg. 9
- ↑ Visions of Symmetry, pg. 78